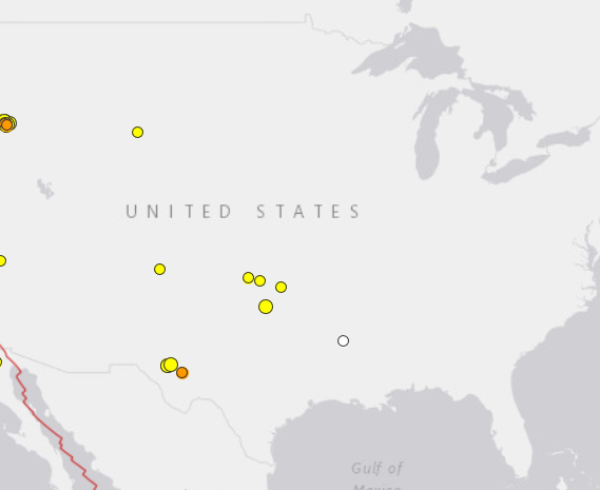
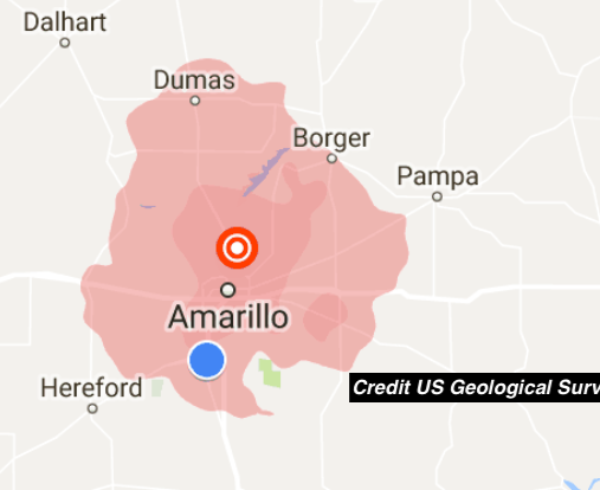
EnergyMakers AG’s Underground Injection and Seismicity Operational Risk Report does a deep dive into induced seismicity—and how fluid injection from oilfield activities and wastewater disposal activities might induce felt earthquakes in certain geologic conditions.
According to Myths and Facts by J.L. Rubinstein (USGS) and A.B. Mahani (Geological Survey of Canada), there are four major ways that fluid injection can induce earthquakes:
- Fluid injection raises the pore-fluid pressure within a pre-existing fault. An earthquake at such a fault would likely have occurred someday, but injection speeds up the process.
- The injection of fluids fills and compresses fluids within pore spaces, causing deformation.
- Injection of fluid that is colder than the rock into which it is being injected causers thermoelastic deformation.
- Fluid injected adds mass to the injection formation.
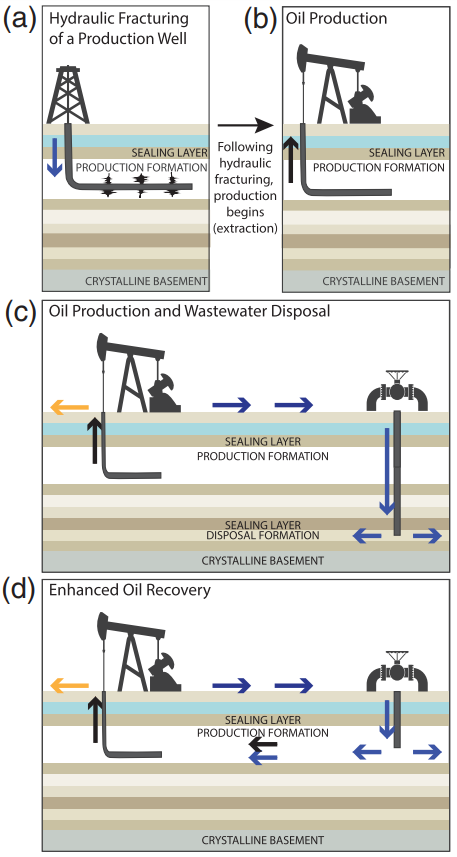
If you are interested in topics related to regional induced seismicity, and general underground injection risk management opportunities, check out our comprehensive Underground Injection Risk Report today to learn more about these fluid injection mechanisms, and how to avoid them.
—
Source: Rubinstein, Justin & Mahani, Alireza. (2015). Myths and Facts on Wastewater Injection, Hydraulic Fracturing, Enhanced Oil Recovery, and Induced Seismicity. Seismological Research Letters. 86. 1060-1067. 10.1785/0220150067.